Bloating is one of the more embarrassing and uncomfortable feelings you can experience. It's also one of the lesser known symptoms of anxiety. While not all bloating is caused by anxiety, there are many cases when anxiety causes bloating, and when bloating can actually lead to further anxiety.
This article will explore the relationship between anxiety and bloating and what you can do to decrease the effects of these symptoms in your day to day life.
Bloating and Anxiety
Anxiety does not cause all bloating episodes. Bloating itself is often a problem with digestion, and one that can affect anyone at any time depending on what you eat, when you eat it, and numerous other factors.
When your bloating is accompanied by other anxiety symptoms, it's highly likely that anxiety is to blame.
What is Bloating?
Bloating is swelling or sensations of fullness caused by air or gas, typically in your stomach or chest. It may lead to burping or flatulence. It may also cause chest pains, abdominal pains and pressure, and more.
The Many Ways Anxiety Causes Bloating
Bloating is actually a very common symptom of anxiety, especially for those with anxiety attacks. What's interesting is that many different issues can cause bloating including, but not limited to:
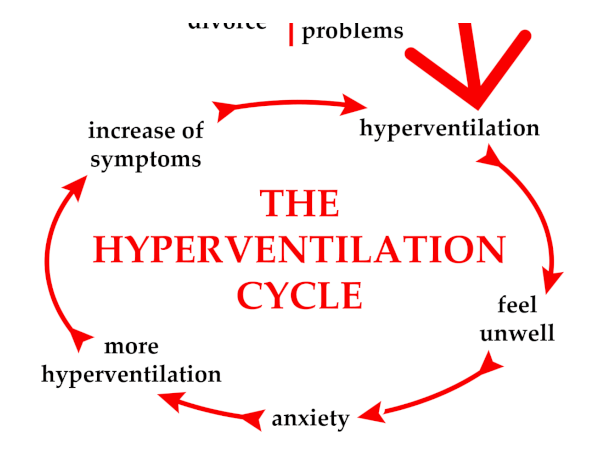
- Hyperventilation The main reason that anxiety leads to bloating is the result of hyperventilation. Hyperventilation is when you take in more air than you need. Hyperventilation causes several additional anxiety symptoms, but both before and after hyperventilation it's not uncommon to feel pressure in your stomach and possibly experience burping.
- General Air Breathing Similarly, even without hyperventilation, you may find that you start to over-breathe during anxiety attacks and swallow more oxygen than necessary, especially if you're prone to swallowing during these attacks. Swallowing oxygen is known to bloat your stomach, and may lead to significant belching and stomach tension.
- Affected Digestion It's also possible for anxiety to affect digestion. Anxiety shuts down a part of the brain that handles digesting food. Stress itself puts a great deal of pressure on your stomach and abdomen, and upsets hormone and neurotransmitter balance. That may create an environment where foods that could normally be digested easily end up being digested poorly, leading to the creation of gas and bloating.
These are some of the most common ways that anxiety creates bloating, and the reason that so many of those living with anxiety every day suffer from severe bloating symptoms.
How Bloating Causes Anxiety
It should be noted, however, that bloating can also cause anxiety. Once again, this is especially true for those that have panic disorder (but it may also occur in anyone with anxiety). Bloating causes many symptoms that can create fear in the person struggling with the gas and air, including:
- Chest Pains
- Nausea
- Stomach Pressure
- Stomach Pain
These symptoms can mimic those of more serious diseases, and pain itself can cause anxiety on its own. They may also trigger panic attacks, because the symptoms may cause people to focus too much on their bodily sensations and fear of a serious health problem. In some cases, the panic attack caused by bloating can lead to hyperventilation, which leads to further bloating.
Ways to Stop the Bloating
Once the air is in your system, the best way to get it out is to try to belch or release flatulence. Holding the air in will simply lead to further pain, and that pain will likely contribute to further anxiety and discomfort. Most gas caused by hyperventilation is scentless, so embarrassment should be less severe, but gas caused by indigestion can be highly scented so finding a bathroom may be in your best interests.
There are a few over the counter medications that can reduce the feeling of bloating, especially if it's caused by indigestion. Some people find that Pepto-Bismol and other antacids provide some relief. The relief is only temporary, however, and may not affect those that experience bloating from air swallowing.
If you feel the bloating is occurring as a result of hyperventilation, you'll also need to make sure that you're not promoting further hyperventilation. While hyperventilating, the body has a tendency to want to breathe in more air, faster. Fight this feeling and try to slow down your breathing, resisting the urge to yawn a lot or breathe quickly.
Fix Bloating From Anxiety
All of these can provide some relief from bloating, but won't prevent bloating from coming back. You can also check your trigger foods, and see if there are foods that tend to cause more bloating when you're anxious.
SUMMARY:
Anxiety affects the gut, it affects breathing, and it affects sleep. All of these things can lead to bloating, and what adds to the complications is that bloating can also affect anxiety. Once you feel bloat, you often have to just let it and fade away, but eventually it will become important to address the anxiety itself.